Tractor-tutorial
Visualization of Tractor Summary Statistics
Tractor is a local-ancestry-aware GWAS tool that produces summary statistics in a single file, including p-values and effect sizes for all haplotypic ancestral terms in your cohort.
Detailed descriptions of the output columns are available in Tractor GWAS local implementation.
In this guide, we demonstrate how to generate Manhattan and Q-Q plots using ggplot2 for summary statistics generated using Tractor. We use ggplot2 for Manhattan plots as it offers superior customization options. An example code snippet is provided below to help you get started.
Note: P-values can vary substantially between phenotypes. Some datasets may have closely clustered values, while others may contain extreme outliers. You may need to adjust the Y-axis or code to suit your specific dataset, but it’s a great place to get started.
Customizing the Y-axis
You can modify the y-axis using scale_y_continuous(), for example by setting breaks and labels:
# Example:
scale_y_continuous(
# breaks = scale_y_breaks,
# labels = scale_y_labels
)
Applying Transformations on Y-axis
To handle outliers and improve readability, you can apply a transformation to the y-axis (e.g., log-scale):
scale_y_continuous(
# transform = log10, # Transform y-axis to log scale, or loglog scale if required.
)
- Reference: ggplot2 scale_continuous documentation
Generating Manhattan and QQ Plots
The following code demonstrates how to create a Manhattan and Q-Q plots from Tractor summary statistics. The code will generate plots for all ancestral terms within the summary statistics.
# Load required packages
library(data.table)
library(dplyr)
library(ggplot2)
library(CMplot)
# Replace below
setwd("/.../.../.../")
sumstats_file <- "/path/to/xxxxxx_sumstats.txt.gz"
# Identify p-value columns
df_header <- fread(sumstats_file, nrows = 0)
pvalue_cols <- grep("^pval_", names(df_header), value = TRUE)
anc_list <- sub("^pval_", "", pvalue_cols)
selected_cols <- c("CHR", "POS", "ID", pvalue_cols)
# Read summary statistics file, and set constants
df_sumstats <- fread(
sumstats_file,
select = selected_cols
)
chr_col <- "CHR"
pos_col <- "POS"
id_col <- "ID"
threshold <- 5e-8
suggestive_threshold <- 1e-5
x_label <- "Genomic position"
y_label <- expression(paste(-log[10], "P"))
colors <- c("skyblue", "lightpink")
ylim_cap <- 5 # padding for y-axis
ouptut_prefix <- "tmp_tractor_phenotype"
# Function for Lambda GC calculation (assumes no 0's in p-values)
compute_lambda_from_pval <- function(pvals) {
pvals <- na.omit(as.numeric(pvals)) # Extract p-values and remove NAs
# pvals[pvals == 0] <- min(pvals[pvals > 0], na.rm = TRUE) # replace zeros (carried out outside this function)
chisq_vals <- qchisq(1 - pvals, df = 1) # Convert p-values to chi-squared statistics
lambda <- median(chisq_vals) / qchisq(0.5, df = 1) # Calculate lambda GC
return(lambda)
}
# Plot Manhattan + Q-Q plots for all ancestry-specific p-values
for (anc in anc_list) {
pval_col <- paste0("pval_", anc)
subset_cols <- c(chr_col, pos_col, id_col, pval_col)
# Subset relevant columns
df <- df_sumstats %>% select(all_of(subset_cols))
# Drop NA values (primarily filter for any rows with p-values as NA)
initial_row_count <- nrow(df)
columns_to_check <- c(chr_col, pos_col, pval_col)
for (col in columns_to_check) {
na_count <- sum(is.na(df[[col]]))
if (na_count > 0) {
df <- df %>% filter(!is.na(!!sym(col)))
cat(paste0("Rows dropped due to NA values in ", col, ": ", na_count, "\n"))
}
}
final_row_count <- nrow(df)
cat(paste0("Total rows dropped: ", initial_row_count - final_row_count, "\n"))
# Replace p-value zeros with minimum non-zero value
if (any(df[[pval_col]] == 0)) {
# min_nonzero <- min(df[[pval_col]][df[[pval_col]] > 0], na.rm = TRUE)
num_zero <- sum(df[[pval_col]] == 0, na.rm = TRUE)
# df[[pval_col]][df[[pval_col]] == 0] <- min_nonzero
df[[pval_col]][df[[pval_col]] == 0] <- .Machine$double.eps
cat(paste0("Replaced ", num_zero, " zero p-values with .Machine$double.eps (",
.Machine$double.eps, ") in ancestry ", anc, "\n"))
}
# # Uncomment below to replace p-values near 1. (Replaces all p-values>0.98 to 0.98)
# if (any(df[[pval_col]] > 0.98)) {
# # max_nonone <- max(df[[pval_col]][df[[pval_col]] < 1], na.rm = TRUE)
# num_one <- sum(df[[pval_col]] > 0.98, na.rm = TRUE)
# df[[pval_col]][df[[pval_col]] > 0.98] <- 0.98
# # df[[pval_col]][df[[pval_col]] == 1] <- max_nonone
# cat(paste0("Replaced ", num_one, " p-values > 0.98 to ",
# 0.98, " in ancestry ", anc, "\n"))
# }
# QQ Plot: Compute Lambda GC
lambda_gc <- compute_lambda_from_pval(df[[pval_col]])
cat(paste0("Lambda GC for ", anc, ": ", round(lambda_gc, 4), "\n"))
# Manhattan Plot: Calculate cumulative positions per chromosome (Used for X-axis label centering)
df_cum <- df %>%
arrange(!!sym(chr_col), !!sym(pos_col)) %>%
group_by(!!sym(chr_col)) %>%
summarise(max_bp = max(!!sym(pos_col))) %>%
mutate(bp_add = lag(cumsum(as.numeric(max_bp)), default = 0)) %>%
select(!!sym(chr_col), bp_add)
df <- df %>%
inner_join(df_cum, by = chr_col) %>%
mutate(cum_pos = !!sym(pos_col) + bp_add)
# Manhattan Plot: Create axis set for chromosome centering
axis_set <- df %>%
group_by(!!sym(chr_col)) %>%
summarize(center = mean(cum_pos))
# Manhattan Plot: Calculate y-axis limits
ylim <- df %>%
filter(!!sym(pval_col) == min(!!sym(pval_col), na.rm = TRUE)) %>%
mutate(ylim = abs(floor(log10(!!sym(pval_col)))) + ylim_cap) %>%
pull(ylim)
# Manhattan Plot: Maximum cumulative position for x-axis limits
max_bp_cum <- max(df$cum_pos, na.rm = TRUE)
# Plot Manhattan plot
manhattan_plt <- df %>%
ggplot(aes(x = cum_pos, y = -log10(!!sym(pval_col)))) +
geom_point(aes(color = factor(!!sym(chr_col) %% 2)), size = 0.25) +
scale_color_manual(values = colors) +
scale_x_continuous(
label = axis_set[[chr_col]],
breaks = axis_set$center,
limits = c(0, max_bp_cum),
expand = expansion(0, 0)
) +
scale_y_continuous(
expand = expansion(0, 0),
# trans = <add_transformation_function / replace "y = -log10(!!sym(pval_col))">, # To transform y-axis, e.g. to be in log scale.
# breaks = scale_y_breaks, labels = scale_y_labels, # Manually offer exact breaks and labels for y-axis
limits = c(0, ylim)
) +
geom_hline(yintercept = -log10(threshold), color = 'gray30', linetype = 'solid') +
geom_hline(yintercept = -log10(suggestive_threshold), color = "gray40", linetype = 'dashed') +
annotate(
"text", x = max_bp_cum, y = -log10(threshold) + 0.4,
label = paste("p-value:", format(threshold, scientific = TRUE)),
hjust = 1, color = "gray50"
) +
annotate(
"text", x = max_bp_cum, y = -log10(suggestive_threshold) + 0.4,
label = paste("p-value:", format(suggestive_threshold, scientific = TRUE)),
hjust = 1, color = "gray50"
) +
labs(x = x_label, y = y_label) +
theme_minimal() +
theme(
panel.grid = element_blank(),
legend.position = "none",
axis.line = element_line(),
axis.ticks = element_line(),
axis.text.x = element_text(size = 14),
axis.text.y = element_text(size = 14)
)
ggsave(
filename = paste0(ouptut_prefix, "_", anc, ".png"),
plot = manhattan_plt,
width = 15, height = 6, dpi = 900, bg = "transparent"
)
# QQ plot using CMplot
output_filename <- paste0(ouptut_prefix, "_qq_", anc)
# CMplot expects input dataframe in the format of genomic marker names, chromosome,
# position, and p-values in rest of the columns
df <- df %>% select(!!sym(id_col), !!sym(chr_col), !!sym(pos_col), !!sym(pval_col))
CMplot(df, type="q",
col = c("#6A3D58", "#CBC3E3"),
plot.type = c("q"), LOG10 = TRUE,
cex = c(0.5, 0.7, 0.5), amplify = FALSE,
signal.cex = 0.72, signal.pch = NULL, chr.den.col = NULL,
threshold = c(suggestive_threshold, threshold),
threshold.lty = c(1, 2), threshold.lwd = c(1, 1),
threshold.col = c("grey","black"),
verbose = TRUE,
width = 6, height = 6,
main = paste("QQ Plot - Ancestry:", anc),
main.cex = 1,
file = "png",
dpi = 300,
file.output = TRUE,
file.name = output_filename)
}
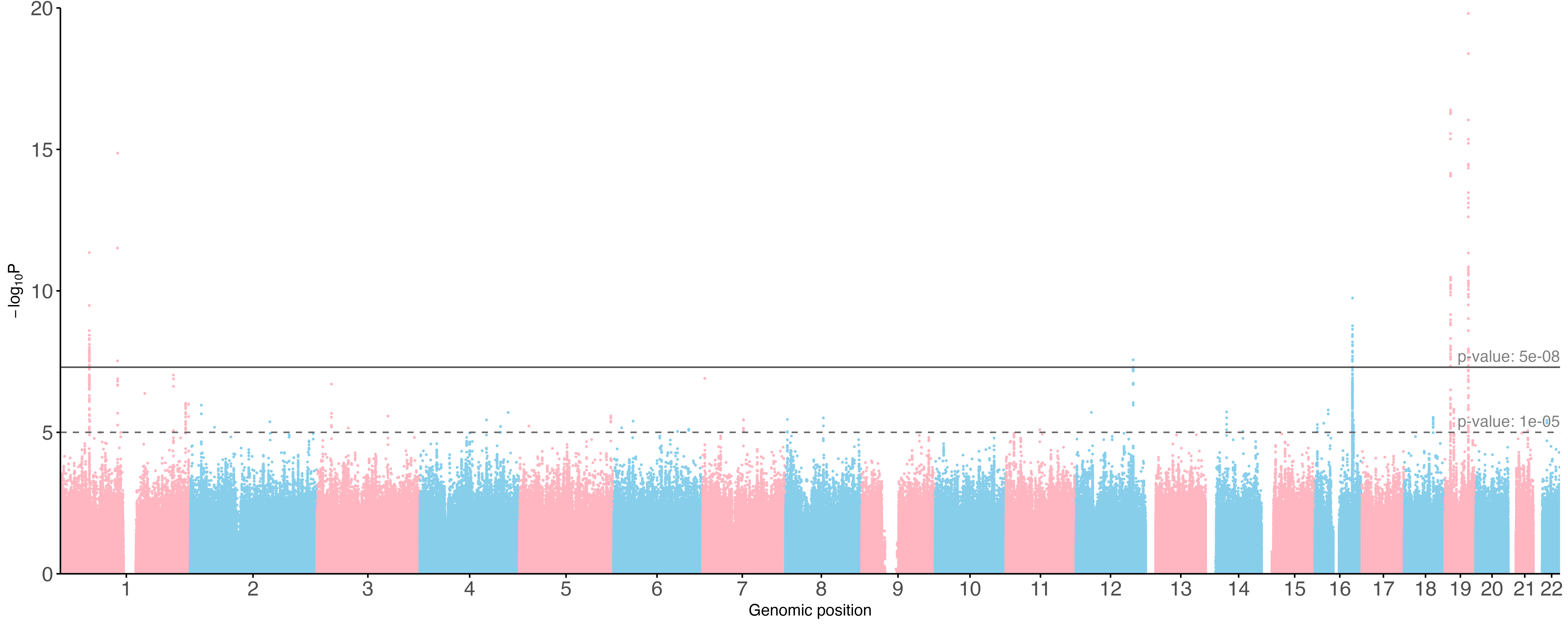
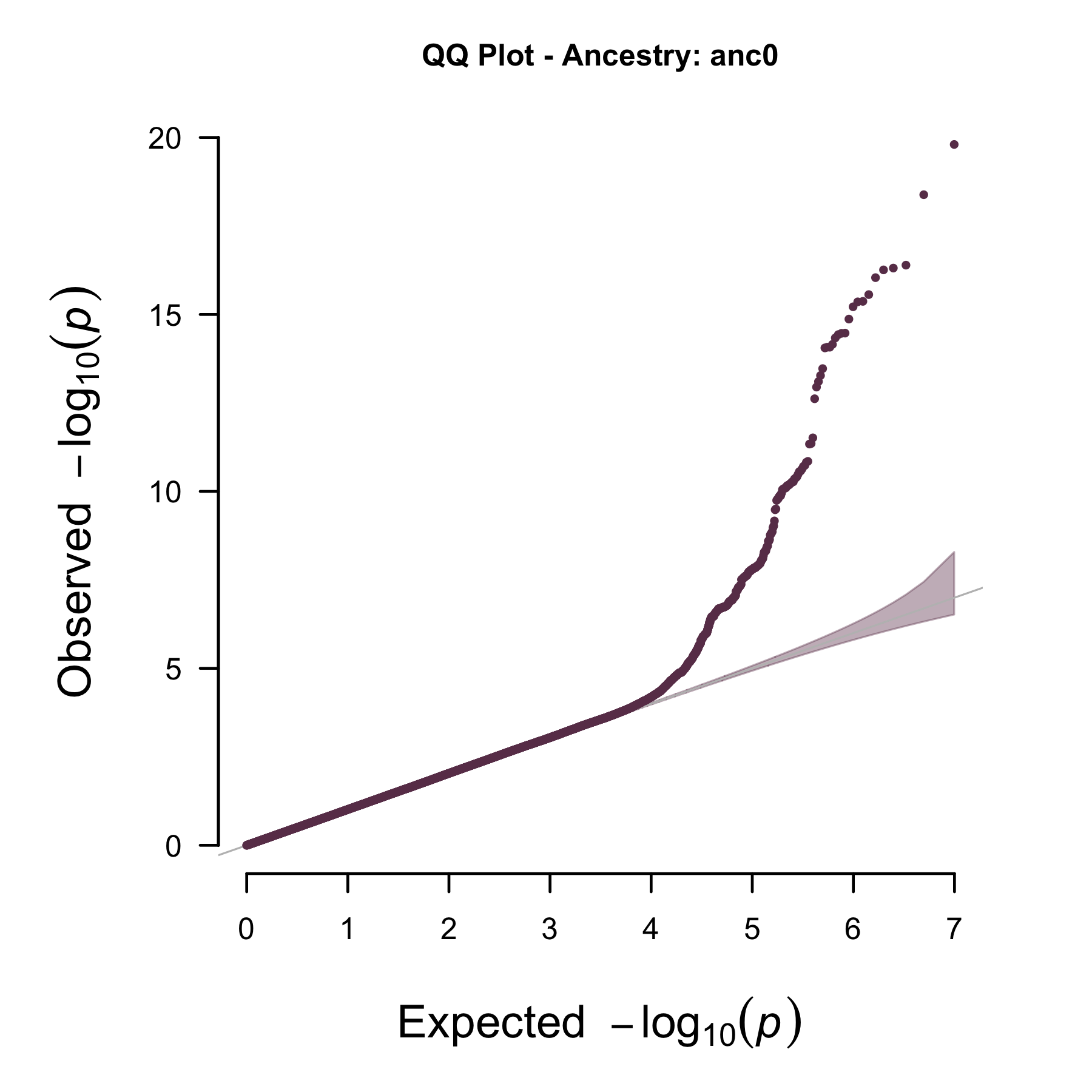
Example plots:
Example Manhattan plot:
Example QQ plot:
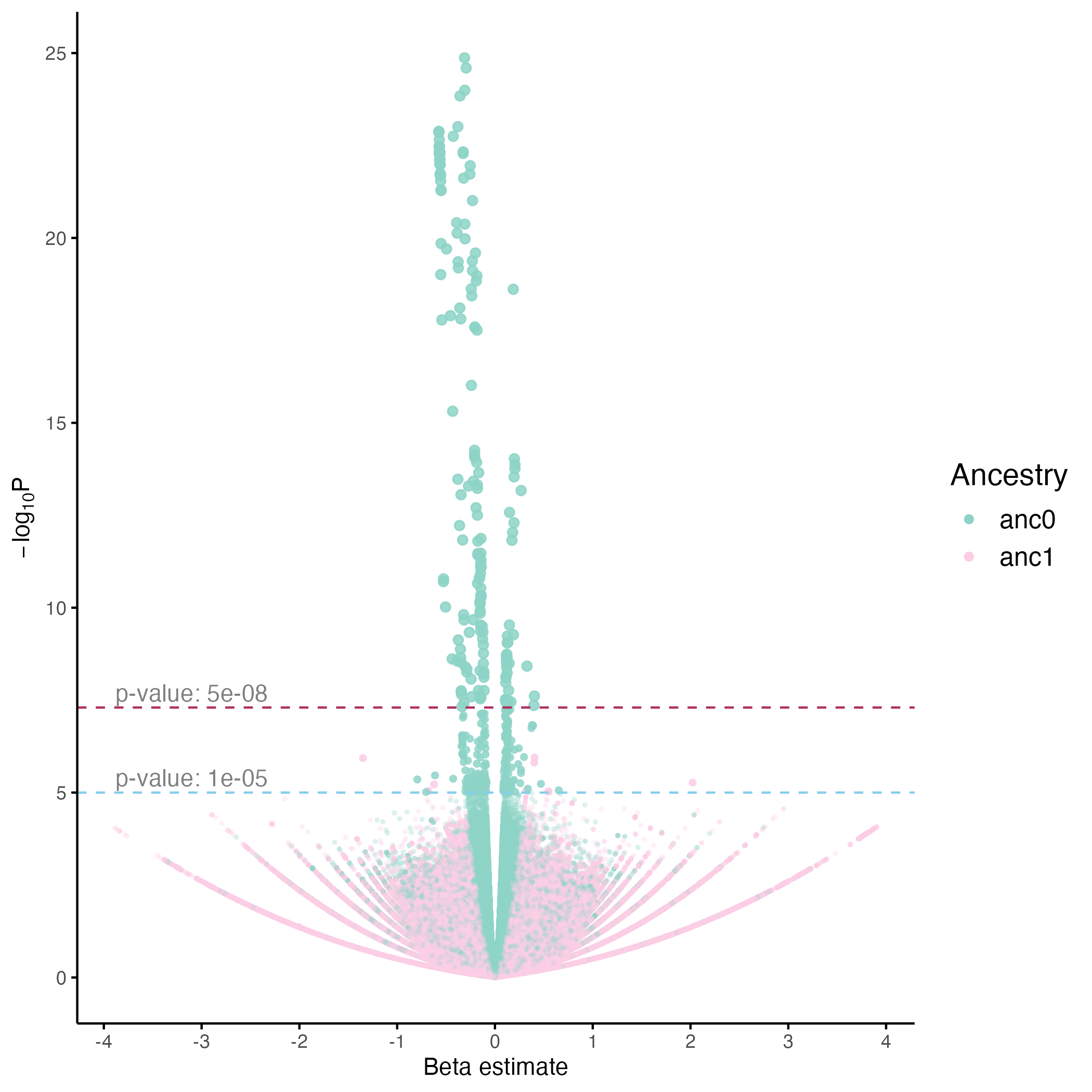
Generating Volcano Plot to study effect sizes
To better explore and identify potential candidate variants, we provide example code to generate a Volcano plot illustrating the relationship between statistical significance (p-values) and effect sizes (β coefficients). By visualizing variants across these dimensions, researchers can more easily pinpoint those that are statistically significant and may indicate variants with potentially meaningful biological effects.
# Load necessary packages
library(data.table)
library(dplyr)
library(tidyr)
library(ggplot2)
library(RColorBrewer)
# Replace below
setwd("/.../.../.../")
sumstats_file <- "/path/to/xxxxxx_sumstats.txt.gz"
# Set paths/required variables
threshold <- 5e-8
suggestive_threshold <- 1e-5
x_label <- "Beta estimate"
y_label <- expression(paste(-log[10], "P"))
output_file <- "tractor_effectsize_volcanoplot.png"
# Identify key columns
df_header <- fread(sumstats_file, nrows = 0)
pvalue_cols <- grep("^pval_", names(df_header), value = TRUE)
beta_cols <- grep("^beta_", names(df_header), value = TRUE)
anc_list <- sub("^pval_", "", pvalue_cols)
selected_cols <- c("CHR", "POS", "ID", pvalue_cols, beta_cols)
# Read summary statistics for specific columns
df_sumstats <- fread(sumstats_file, select = selected_cols)
# Reshape to long format (auto-detects pval/beta pairs)
df_long <- df_sumstats %>%
pivot_longer(
cols = all_of(c(pvalue_cols, beta_cols)),
names_to = c(".value", "Ancestry"),
names_pattern = "(pval|beta)_(.*)"
)
# Add new columns: threshold, transparency and size of points in the plot.
df_long <- df_long %>%
filter(!is.na(pval)) %>% # Remove rows where pval is NA
mutate( y_val = -log10(pval),
threshold_level = case_when(
y_val >= -log10(threshold) ~ "Genome-wide",
y_val >= -log10(suggestive_threshold) ~ "Suggestive",
TRUE ~ "NS"),
point_alpha = case_when( # Set transparency for points
threshold_level == "NS" ~ 0.3, # More transparent for NS
TRUE ~ 0.85),
point_size = case_when( # Set sizing of points
threshold_level == "NS" ~ 0.8,
threshold_level == "Suggestive" ~ 1.4,
threshold_level == "Genome-wide" ~ 1.8)
) %>%
slice_sample(prop = 1) # Shuffle rows
# Dynamic color palette for ancestries
n_anc <- length(unique(df_long$Ancestry))
ancestry_palette <- colorRampPalette(brewer.pal(8, "Set3"))(n_anc)
names(ancestry_palette) <- unique(df_long$Ancestry)
# Y-axis formatting
max_y <- max(df_long$y_val, na.rm = TRUE) + 2
# Plot
vol_plot <- ggplot(df_long, aes(x = beta, y = y_val)) +
geom_point(
aes(color = Ancestry, shape = threshold_level, alpha = point_alpha, size = point_size)
) +
scale_alpha_identity() +
scale_size_identity() +
geom_hline(
yintercept = -log10(threshold),
linetype = "dashed", color = "maroon"
) +
geom_hline(
yintercept = -log10(suggestive_threshold),
linetype = "dashed", color = "skyblue"
) +
scale_color_manual(values = ancestry_palette, name = "Ancestry") +
scale_shape_manual(
values = c("NS" = 16, "Suggestive" = 16, "Genome-wide" = 19),
name = "Significance"
) +
scale_x_continuous(breaks = scales::pretty_breaks(n = 9)) +
scale_y_continuous(breaks = c(seq(0, max_y, by = 5))) +
labs(x = x_label,
y = y_label) +
annotate(
"text",
x = min(df_long$beta, na.rm = TRUE),
y = -log10(threshold) + 0.4,
label = paste("p-value:", format(threshold, scientific = TRUE)),
hjust = 0, color = "gray50"
) +
annotate(
"text",
x = min(df_long$beta, na.rm = TRUE),
y = -log10(suggestive_threshold) + 0.4,
label = paste("p-value:", format(suggestive_threshold, scientific = TRUE)),
hjust = 0, color = "gray50"
) +
theme(
panel.background = element_rect(fill = NA, color = NA),
plot.background = element_rect(fill = NA, color = NA),
panel.grid = element_blank(),
axis.line = element_line(color = "black"),
axis.ticks = element_line(color = "black", linetype = "dashed"),
legend.position = "right",
legend.title = element_text(size = 14),
legend.text = element_text(size = 12),
legend.key = element_rect(fill = "white")
) +
guides(shape = "none")
# Save plot
ggsave(
filename = output_file,
plot = vol_plot,
# width = 8, height = 12,
dpi = 300, bg = "transparent"
)
paste0("Volcano plot saved as: ", output_file)
Example Volcano Plot: